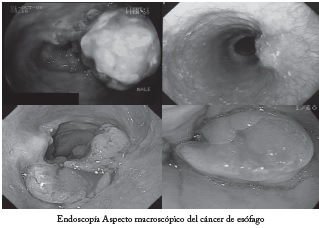
Cáncer de esófago y de la unión gastro-esofágica
comentadores del Relato: Rubens A Sallum, Luis Durand
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31837/relatos/11Palabras clave:
cáncer, esófago, tratamiento quirúrgico, epidemiología, Carcinoma epidermoide, Adenocarcinoma, Esófago-Gastro-Duodeno Doble Contraste, diagnóstico, imagenología, Fibrobroncoscopía, Fibrolaparoscopía, cirugía mini-invasiva, resección esofágica, UruguayResumen
El cáncer de esófago es una patología muy desafiante para el cirujano y para todo el equipo tratante. Es una enfermedad
agresiva, que generalmente en nuestro medio todavía se diagnostica en etapas avanzadas, y que requiere para su
curación de una compleja estrategia multidisciplinaria. La cirugía juega un rol fundamental en la intención curativa de
esta enfermedad, pero es muy demandante desde el punto de vista técnico para el equipo quirúrgico.
Históricamente la supervivencia global luego del diagnóstico de cáncer de esófago, es muy baja, del orden del 10 al 13%
a los 5 años1. Tal es así, que, en la literatura china, antiguamente se describía al paciente con cáncer de esófago como
quien ¨sufre en otoño, y no ve la llegada del verano¨.
Descargas
Citas
Jemel A, Murray T, Samuels A, et al. Cancer statics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clinics 2003; 53:5-26.
Orringer MB, Marshall B, Iannettoni MD: Transhiatal esophagectomy: Clinical experience and refinements. Ann Surg 230:229-400, 1999.
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H: Radical lymph node dissection for cancero f the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 1994;220:364-72.
Siewert JR, Feith M, Stein HJ. Esophagectomy as therapeutic principle for squamous cell esophageal cancer. Chirurg. 2005Nov; 76 (11):1033-43.
Portale G, Hagen A, DeMeester T. Modern 5-year survival of respectable esophageal adenocarcinoma: Single Institution Experience
with 263 patients. J Am Coll Surg Vol 202 (4) April 2006.
Deng HY, Huang WX, Li G, et al. Comparison of short-term outcomes between robot-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy
and video-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy in treating middle thoracic esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2018Aug 1;31(8)
Santiago, P. Beraldo, G. Varela, M. Reyes, S. Cubas, S. Taroco, L. Cirugía del cáncer de Esófago, 10 años de experiencia en el hospital central de las FFAA. Trabajo presentado en el 64 Congreso Uruguayo de Cirugía. Noviembre 2013. Montevideo. Premio “Ardao” 2013 de la Sociedad de Cirugía del Uruguay.
Siewert JR, Stein HJ. Carcinoma of the cardia: carcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction—classification, pathology and extent of resection. Dis Esophagus 1996; 9:173-82.
Orringer MB., Marshall B., Chang AC., et all. Two Thousand Transhiatal Esophagectomies Changing Trends, Lessons Learned.Ann Surg 2007 Sep; 246(3): 363–374.
Vivas C, Neirotti R, Caviglia P, Giossa W, Rodríguez JL. Diez años de experiencia en la cirugía del cáncer de esófago. RevHosp. Maciel 1997; 2:4-8.
Piacenza G, Bergalli L, Carriquiry L. Esofagectomía sin toracotomía en el tratamiento del neoplasma de esófago. Cir Uruguay1987; 57(2-3); 93-101.
Fernández R, Henderson E, Rodríguez G, y col. Vaciamientos ganglionares en las neoplasias digestivas. Cir Uruguay2003,73(1):13-52.
Misa R, Taruselli R, Santandreu J, Vázquez A, Morelli R. Esofagectomía transhiatal. Experiencia del Hospital Pasteur en suaplicación en el cáncer de esófago inferior. Cir Uruguay 1997; 67: 155-161.
González D, Vega A, Monti J, Di Leoni F, Torres M. Tratamiento quirúrgico del cáncer de esófago. Procedimiento de IvorLewis. Cir Uruguay 2004, 74(3): 165-8.
Santiago P, Beraldo G, Cabillon J, Taroco L. Cirugía de Resección del Esófago. Experiencia en el HCFFAA. Trabajo Presentado en la Sociedad de Cirugía del Uruguay en Junio de 2006.
Barrios E. Registro Nacional del Cáncer. Comisión Honoraria de Lucha Contra el Cáncer. Situación Epidemiológica del Uruguay en Relación al Cáncer. Mayo 2018.
Fok M., Wong John. Cáncer de Esófago. Operaciones Abdominales. Maingot. Ed 10. Pag 796-820. Editorial Médica Panamericana.1997.
Taruselli R., Escobar P., Guarnieri C., Voliovici E. Tratamiento Multimodal del Cáncer de Esófago. Mesa Redonda de Clínica Quirúrgica A. 69 Congreso Uruguayo de Cirugía. Octubre 2018. (Datos no publicados).
Cancer. List of classifications by cancer sites with sufficient or limited evidence in humans; 2014. p. 1–105.
Andrici J, Eslick GD. Mate consumption and the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-anal- ysis. Dis Esophagus.
;26(8):807–16.
Lubin JH, De Stefani E, Abnet CC, et al. Mate drink- ing and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in South America: pooled
results from two large multicenter case-control studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2014;23(1):107–16.
Bennett MK. Pathology of bening, malignant and premalignant oesophageal and gastric tumours. Oesophagogastric Surgery.Ed: Griffin SM., Raimes SA. Third Edition. ELSEVIER SAUNDERS. Chap 1. Pag 1-25. 2006.
Liu J, Wang J, Leng Y, et al. Intake of fruit and veg- etables and risk of esophageal squamous cell carci- noma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(2):473–85.
Sitas F, Egger S, Urban MI, et al. InterSCOPE study: associations between esophageal squamous cell carci- noma and human
papillomavirus serological markers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(2):147–58
Chen X, Yuan Z, Lu M, et al. Poor oral health is asso- ciated with an increased risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma -a population-based case-control study in China. Int J Cancer. 2017;140(3):626–35
Streitz JJ., Ellis FJ., Gibb SP et al. Achalasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: analysis of 241 patients. AnnThorac Surg 1995; 59 (6): 1604-9.
Zaninotto G, Rizzetto C, Zambon P, et al. Long-term outcome and risk of oesophageal cancer after surgery for achalasia. BrJ Surg. 2008 Dec;95(12):1488-94.
Contini S, Scarpignato C. Caustic injury of the upper gastrointestinal tract: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol.
Jul 7;19(25):3918-30.
Iwaya T, Sawada G, Amano S, et al . Downregulation of ST6GALNAC1 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
development. Int J Oncol. 2017 Feb;50(2):441-447.
Novacek G .Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006 Sep 15; 1:36.
Wang L, Yu X, Li J, Zhang Z, Hou J, Li F Prognostic significance of p53 expression in patients with esophageal cancer: ameta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 1;16:373.
Lagergren J., Bergstrom R., lindren A et al. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Important confirmation in a case-controlled study that symptomatic reflux reflux oesophagitis leads to adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. N Engl J Med 1999; 340:825-31.
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, et al. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of pprospective observational stud- ies. Lancet. 2008; 371:569–78
Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S. Epidemiolo¬gy of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 2005; 54: 710-717.
Cameron AJ., Lomboy CT. Barrett´s esophagus: age, prevalence and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology 1992;103:1241-5.
Lieberman DA. Risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in community-based practice. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:1293–7.
Oberg S, Ritter MP, Crookes PF, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and mucosal injury with emphasis on short-segmentBarrett’s esophagus and duodenogastroesophageal reflux. J Gastrointest Surg. 1998; 2:547–53.
Theisen J, Peters JH, Fein M, et al. The mutagenic potential of duodenoesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 2005; 241:63–8.
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol.
; 111:30–50.
Desai TK, Krishnan K, Samala N, et al. The incidence of oesophageal adenocarcinoma in non-dysplastic Barrett’s oesophagus:a meta-analysis. Gut. 2012; 61:970–6
Singh S, Manickam P, Amin AV, et al. Incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus with low-grade dysplasia:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:897–909.
Rastogi A, Puli S, El-Serag HB, et al. Incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and high-grade dysplasia: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:394–8.
Edelstein ZR, Farrow DC, Bronner MP, et al. Central Adiposity and risk of Barrett´s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2007;133:403-11.
Hampel H, Abraham NS, El-Serag HB. Meta-analysis: obesity and the risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications.
Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143: 199-211.
Ye W, Langergren J, Engstrand L, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric athophy: risk of adenocarcinoma and aquamous
cell carcinoma of the esophagus and adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004; 96: 388-96.
Rokkas T, Pistiolas D, Sechopoulos P, et al. Relatioship between Helicobacter pylori infection and esophageal neoplasia: ameta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 5:1413-7.
Polyzos SA., Zeglinas C., Artemaki F., et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and esophageal adenocarcinoma: a review and apersonal view. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan-Feb; 31(1): 8–13.
Pinotti HW, Cecconello I, Aissar Sallum R, Santo MA. Cancer of the Esophagogastric Junction. Diagnosis and Treatment.First Ed. Prol Ed. Chapter 3. Pag 30-39. 2010.
Fernandez Esparrach G, Castells Garangou A. Tumores Malignos del Esófago. Cáncer Digestivo, patogenia, diagnóstico,tratamiento y prevención. Ed Castells A, Balaguer R. ELSEVIER. 2014. Cap 16. Pag 251-258.
Shujuan Y., Siying W., Yuchuan H. Et al. Pruebas de detección para el cáncer de esófago. Cochrane. Base de Datos de Revisiones
Sistemáticas. Versión Publicada 12 diciembre 2012.
Nguyen N. Current aplication of confocal endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal disorders. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 23:1-9.
Pérez N., Quintero E., Parra Blanco A. Cribado del carcinoma escamoso de esófago en población de riesgo. Gastroenterología
y Hepatología. Vol 28. Num 6. Jun 2005. Pag 311-364.
Saunders HS., Wolfman NT., Ott DJ. Esophageal cancer. Radiologic staging. Radiol Clin North Am 1997;35 (2):281-94.
Botet JF., Ligthdale CJ., Zauber AG., et al. Preoperative staging of esophageal cancer: comparison of endoscopic US and
dynamic CT. Radiology 1991;181:419-25.
Wu LF., Wang BZ., Feng JL., et al. Preoperative TN staging of esophageal cancer: comparison of mini-probe ultrasonography,
spiral CT and MRI. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9:219-24.
Nakashima K., Nakashima A., Seto H., et al. Thoracic esophageal carcinoma: evaluation in the sagittal section with magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 1997; 22 (1):20-3.
Catalano MF., Sivak MV., Rice T., et al. Endosonographyc features, predictive of lymph node metastasis. Gastrointest Endosc1994; 40:442-6.
Yoon YC., Lee KS., Shim YM., et al. Metastasis to regional lymph nodes in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:CT vs FDG PET for presurgical detection prospective study. Radiology 2003:227(3):764-70.
NCNN Clinical Practice in Oncology. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers. Version 2.2018-May 22,2018.
NCNN Clinical Practice in Oncology. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers. Version 2.2019-July,2019.
Wang F, Shen LY, Ma SH, Li N, et al. Advantages of positron emission tomography-computed tomography imaging in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Diseases of the Esophagus (2013) 26, 832–837 .
Wenyao Z, Yan Z, and Jinming Y. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography predicts lymph node responses to definitive chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients OncoTargets and Therapy. 25 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4345-4353.
Zum Büschenfelde CM, Herrmann K, Schuster T. (18)F-FDG PET-guided salvage neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy of adenocarcinoma
of the esophagogastric junction: the MUNICON II trial. J Nucl Med. 2011 Aug;52(8):1189-96.
Borggreve AS, Mook S. Preoperative image-guided identification of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal cancer (PRIDE): a multicenter observational study. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18: 1006.
Noordman BJ, BPL W, Lagarde SM, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus active surveillance for oesophageal
cancer: a stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4034-1.
Comparison of Systematic Surgery Versus Surveillance and Rescue Surgery in Operable Oesophageal Cancer with a Complete Clinical Response to Radiochemotherapy (Esostrate). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02551458.
Watt I., Stewart I., Anderson D., et al. Laparoscopy, ultrasound and computed tomography in cancer of the esophagus and cardia: a prospective comparison for detecting intra-abdominal metastases. Br J Surg 1989; 76:1036-9.
Dagnini G., Caldironi MW., Marin G et al. Laparoscopy in abdominal staging of esophageal carcinoma. Report of 369 cases.Gastrointest Endosc. 1986; 32:400-402.
Hayes T., Smyth E., Riddell A., Allum W. Staging in Esophageal and Gastric Cancers. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 31 (2017)427–440.
Convie L, Thompson RJ, Kennedy R, et al. The current role of staging laparoscopy in oesophagogastric cancer. Ann R Coll
Surg Engl. 2015 Mar;97(2):146-50.
Strandby RB, Svendsen LB, Fallentin E, et al. The Multidisciplinary Team Conference's Decision on M-Staging in Patients with Gastric- and Gastroesophageal Cancer is not Accurate without Staging Laparoscopy. Scand J Surg. 2016 Jun;105(2):104-8.
Gerhard M., Juhl H., Kalthoff H., et al. Specific detection of carcinoembryonic antigen-expressing tumor cells in bone marrow
aspirates by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12(4): 725-9.
Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, et al. Prediction of survival with squamous cell carcinoma antigen in patients with resectable
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 2003 May;133(5):486-94.
Tanaka K, Yano M, Motoori M, et al. CEA-antigen and SCC-antigen mRNA expression in peripheral blood predict hematogenous
recurrence after resection in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010 Oct;17(10):2779-86.
Dreilich M, Wanders A, Brattstrom D, et al. HER-2 overexpression (3+) in patients with squamous cell esophageal carcinoma
correlates with poorer survival. Dis Esophagus 2006; 19:224-231.
Schoppmann SF, Jesch B, Friedrich J, et al. Expression of Her-2 in carcinomas of the esophagus. Am J Surg Pathol 2010;
:1868-1873.
Editors: Amin MB., Edge S., Greene F., et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th Edition. 2017.
Rice TW, Kelsen D, Blackstone EH, et al.: Esophagus and Esophagogastric Junction. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, etal., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 185-202.
Oesphagus including oesophagogastric junction. In: Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK, Wekind C, eds. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. International Union Against Cancer. 8th ed. Oxford, England: Wiley; 2017: 57–62.
Rice TW., Pati DT, Blackstone EH. 8th edition AJCC/UICC staging of cancers of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction:
application to clinical practice. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;6(2):119-30.
Cools-Lartigue J., Molena D., Gerdes H. Staging of Esophageal Cancer: Implications for Therapy. Schlottmann F et al. (eds.),
Esophageal Cancer. Diagnosis and Treatment. Chap 4. P 29-42. 2018.
Durand L., De Antón R., Rossi C., et al. Nueva clasificación para el pronóstico del cáncer de esófago. Novedades de la 8va edición de la clasificación TNM. www.sact.org.ar/revista/2018/mayo/3.pdf.
van Vliet EP, Eijkemans MJ, Kuipers EJ, Hermans JJ, Steyerberg EW, Tilanus HW, van der Gaast A, Siersema PD. A comparison between low-volume referring regional centers and a high-volume referral center in quality of preoperative metastasis detection in esophageal carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Feb;101(2):234-42.
Casson AG, van Lanschot JJ. Improving outcomes after esophagectomy: the impact of operative volume. J Surg Oncol. 2005Dec 1;92(3):262-6.
Rouvelas I, Zeng W, Lindblad M, Viklund P, Ye W, Lagergren J. Survival after surgery for oesophageal cancer: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2005 Nov;6(11):864-70.
Gillison EW, Powell J, McConkey C, SpychaL R. Surgical workload and outcome after resection for carcinoma of the oesophagusand cardia. Br J. Surg 2002 Mar; 89(3):244-8.
Branagan, G.; Davies, N. Early impact of centralization of oesophageal cancer surgery services. Br J Surg Vol 91(12), December2004, p 1630–1632.
Dimick J, Cattaneo S, Lipsett P, Pronovost P, Heitmiññer R. Hospital volume is related to clinical and economic outcomes of
esophageal resection in Maryland. Ann Thorac Surg 2001 Aug; 72(2):334-9.
Khuri S, Hussaini B, Kumbhani D, Healey N, Henderson W. Does Volume help Predict Outcome in Surgical Disease? Advances
in Surgery Vol. 39. 2005: pag 379-453.
Wenner J, Zilling T, Bladstrom A, Alvegard TA. The influence of surgical volume on hospital mortality and 5-years survival for carcinoma of the oesophagus and gastric cardia. Anticancer Res 2005 Jan-Feb; 25(1B): 419-24.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers Version 2.2018 — May 22, 2018.
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, Gerson LB, American College of G. ACG clinical guideline: diagno- sis and management
of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(1):30–50.
Pech O, May A, Manner H, et al. Long-term effi- cacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma
of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(3):652–60. e651.
Lordick F, Mariette C, Haustermans K, Obermannova R, Arnold D, Committee EG. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(suppl 5): v50–7.
AkutsuY, Uesato M, Shuto K, et al. The overall prevalence of metastasis in T1 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective
analysis of 295 patients. 40. Ann Surg. 2013;257(6):1032–8.
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. ACG clinical guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus. Am JGastroenterol 2016:111;30-50.
Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, Gebski V, et al. Surgery alone versus chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for resectable cancer of the oesophagus: a randomised controlled phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2005; 6:659–68.
Oesophageal Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Annals of Oncology 27 (Supplement 5): v50–v57, 2016 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdw329.
Wobst A, Audisio RA, Colleoni M, Geraghty JG. Oesophageal cancer treatment: studies, strategies and facts. Ann Oncol 1998; 9: 951-62.
Robb WB, Naughton P, Walsh TN. Neoadjuvant treatment of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Minerva Chir. 2004; 59:461-70.
Markar SR, Karthikesalingam A, Thrumurthy S, Low DE. Volume-outcome relationship in surgery for esophageal malignancy:
systematic review and meta- analysis 2000–2011. J Gastrointest Surg 2012; 16: 1055–1063.
Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable
oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 681–692.
Kranzfelder M, Schuster T, Geinitz H et al. Meta-analysis of neoadjuvant treatment modalities and definitive non-surgical
therapy for oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Br J Surg 2011; 98: 768–783.
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N
Engl J Med 2012; 366: 2074–2084.
Arnott SJ, Duncan W, Gignoux M, et al. Preoperative radiotherapy in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis using individual
patient data (Oesophageal Cancer Collaborative Group). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998; 41:579-583.
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N
Engl J Med 2012; 366: 2074–2084.
Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJ, Hulshof MC et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal
or junctional cancer (CROSS): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 1090–1098.
Goodman K., Niedzwiecki D., Hall N., et al. Initial results of CALGD 80803 (alliance): a randomized phase II trial of PETscan-directed combined modality therapy for esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 1:35.
Mayangi S., Irino T., Kawakudo H. Et al. Neoadjuvant treatment strategy for locally advanced thoracic esophageal cancer.
Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019;3:269–275.
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. A randomized trial comparing post- operative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and
-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squa- mous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus
(JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68–74.
Nakamura K, Kato K, Igaki H, et al. Three-arm phase III trial com- paring cisplatin plus 5-FU (CF) versus docetaxel, cisplatin
plus 5-FU (DCF) versus radiotherapy with CF (CF-RT) as preoperative therapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer
(JCOG1109, NExT study). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013;43:752–5.
Allum WH., Stenning SP., Bancewicz J., et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial of surgery with or without preoperative
chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Oct 20;27(30):5062-7.
Cunningham D., Allum W., Stenning S., et al. For the MAGIC Trial Participants. Perioperative Chemotherapy versus Surgery Alone for Resectable Gastroesophageal Cancer. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:11-20.
Ychou M., Boige V., Pignon JP., et al. Perioperative chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal
adenocarcinoma: an FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011 May 1; 29(13):1715-21.
Al-Batran SE., Pauligk C., Homann N., et al. Docetaxel, oxaliplatin, and fluorouracil/leucovorin (FLOT) versus epirubicin,
cisplatin, and fluorouracil or capecitabine (ECF/ECX) as perioperative treatment of resectable gastric or gastro-esophageal
junction adenocarcinoma: The multicenter, randomized phase 3 FLOT4 trial (German Gastric Group at AIO). Ann of Oncol. Vol 28 June 2017.
Stahl M., Walz MK., Stuschke M., et al. Phase III comparison of preoperative chemotherapy compared with chemoradiotherapy
in patients with locally advanced adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(6):851.
Hoepnner J., Lordick F, Brunner T. et al. ESOPEC: prospective randomized controlled multicenter phase III trial comparing
perioperative chemotherapy (FLOT protocol) to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol) in patients with
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (NCT02509286). BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 19;16:503. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2564-y.
Stahl M, Stuschke M, Lehmann N, et al. Chemoradiation with and without surgery in patients with locally advanced squamous
cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2310–7.
Bedenne L, Michel P, Bouche O, et al. Chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with Chemoradiation alone in squamous
cancer of the esophagus: FFCD 9102. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1160–8.
Herskovic A, Martz K, al-Sarraf M, et al. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in
patients with cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J Med 1992; 326:1593- 1598.
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, et al. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of
a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA 1999; 281:1623-1627.
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma
of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:725–30.
Ando N, Iizuka T, Kakegawa T, et al. A randomized trial of surgery with and without chemotherapy for localized squamous
carcinoma of the thoracic esoph- agus: the Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997;114:205–9.
Skinner DB. Enbloc resection for neoplasms of the esophagus and cardia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1983; 85:59-71.
Akiyama H. Surgery for cáncer of the oesophagus. Baltimore: Williams-Wilkins, 1990; pp. 43-4 and 223-4.
Wong J. Esophageal resection for cancer: The rationale of current practice. Am J Surg 1987; 153:18-24.
Akiyama H., Tsurumaru M., Udagawa H., et al. Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic oesophagus. AnnSurg 1994; 22:364-73.
Dresner SM., Griffin SM. Pattern of recurrence following radical oesophagectomy with two field lymphadenectomy. Br J Surg 2000; 87:1426-33.
Isono K., Onoda S., Nakayama K. Results of a nationwide study on the three-field lymph node dissection of esophageal cancer. Oncology 1991;48(5):411-20.
Lerut T., Nafteux P., Moons J., et al. Three-field lymphadenectomy for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal
junction in 174 R0 resections: impact on staging, disease-free survival, and outcome: a plea for adaptation of TNM classification in upper-half esophageal carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2004 Dec;240(6):962-72
Alkorki N., Skinner D. Slould en bloc esophagectomybe the standard of care for esophageal carcinoma? Ann Surg 2001;234(5):581-7.
Ma M., Tang P., Jiang H. et al. Number of negative lymph nodes as a prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct;13(5): e278-e283.
Lagergren J., Mattsson F., Zylstra J., et al. Extent of Lymphadenectomy and Prognosis After Esophageal Cancer Surgery.JAMA Surg. 2016 Jan;151(1):32-9.
Rizk NP, Ishwaran H, Rice TW, et al. Optimum lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg 2010;251:46–50.
Gawald KA., Hosch SB., Bumann D., et al. How important is the route of reconstruction after esophagectomy: a prospective randomised study. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94(6): 1490-6.
Bartels SH., Thorbon S., Siewert JR. Anterior vs Posterior reconstruction after transhiatal oesophagectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Surg 1993; 80: 565-80.
Chang AC, Ji H, Birkmeyer NJ, et al. Outcomes after transhiatal and transthoracic esophagectomy for cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;85(2):424-9.
Warner S, Chang YH, Paripati H, et al. Outcomes of minimally invasive esophagectomy in esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014 Feb;97(2):439-45.
Pais C., Murias F., Castro A, y col. Navigare Necesse Est. Resultados del Tratamiento del Cáncer de Esófago. Experiencia Multicéntrica de un mismo equipo quirúrgico. Clínica Quirúrgica 1 Hospital Pasteur. Sesión Científica Sociedad de Cirugía del Uruguay. Julio 2019. https://youtu.be/elQvEdr02Hk.
Valsalgiacomo P., Bentancur M., Pose S., et al. Tratamiento quirúrgico del cáncer de esófago en la era de la cirugía mini-invasiva.
Sesión Científica Sociedad de Cirugía del Uruguay. Clínica Quirúrgica 3. Hospital Maciel. Julio 2019.
Gossot D, Cattan P, Fritsch S, et al. Can the morbidity of esophagectomy be reduced by the thoracoscopic approach? Surg Endosc 1995;9(10):1113-5.
Horgan S, Berger RA, Elli EF, et al. Robotic-assisted minimally invasive transhiatal esophagectomy. Am Surg 2003;69(7):624-6.
Bodner J, Wykypiel H, Wetscher G, et al. First experiences with the da Vinci operating robot in thoracic surgery. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg 2004;25(5):844-51.
Horgan S, Berger RA, Elli EF, et al. Robotic-assisted minimally invasive transhiatal esophagectomy. Am Surg 2003;69(7):624-
Maloney JD, Weigel TL,. Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Malignant and Premalignant Diseases of the Esophagus . Surg Clin N Am 88 (2008) 979–990.
Gurusamy KS, Pallari E, Midya S, Mughal M. Laparoscopic versus open transhiatal oesophagectomy for oesophageal cancer.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 3. Art. No.: CD011390. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011390.pub2.
Luketich JD, Pennathur A, Franchetti Y, et al. Minimally invasive esophagectomy: results of a prospective phase II multicenter
trial-the eastern cooperative oncology group (E2202) study. Ann Surg 2015;261:702-707.
Luketich JD, Alvelo-Rivera M, Buenaventura PO, et al. Minimally invasive esophagectomy: outcomes in 222 patients. AnnSurg 2003;238:486-495.
Biere SS, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Maas KW, et al. Minimally invasive versus open oesophagectomy for patients with oesophageal cancer: a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012;379:1887-1892.
Klevebro F, Scandavini CM, Kamiya S. Single center consecutive series cohort study of minimally invasive versus open resection for cancer in the esophagus or gastroesophageal junction. Diseases of the Esophagus (2018) 31, 1–6 .
Biere SS, Maas KW, Bonavina L. Traditional invasive vs. minimally invasive esophagectomy: a multi-center, randomized trial (TIME-trial). Biere et al. BMC Surgery 2011, 11:2 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2482/11/2.
Coia LR, Soffen EM, Schultheiss TE, et al. Swallowing function in patients with esophageal can- cer treated with concurrent radiation and chemother- apy. Cancer. 1993;71(2):281–6.
Herskovic A, Martz K, Al-Sarraf M, et al. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radio- therapy alone in patients with cancer of the esopha- gus. N Engl J Med. 1992;326(24):1593–8 .
Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2016; 27 (Suppl 5): v38–v49.
Homs MY, Steyerberg EW, Eijkenboom WM et al. Single-dose brachytherapy versus metal stent placement for the palliation
of dysphagia from oesophageal cancer: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2004; 364: 1497–1504.
Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2016; 27 (Suppl 5): v38–v49.
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. Trastuzumab in combina- tion with chemotherapy
versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer
(ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9742):687–97.
Cunningham D, Stenning SP, Smyth EC, Okines AF, Allum WH, Rowley S, et al. Peri-operative che- motherapy with or without bevacizumab in oper- able oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (UK Medical Research Council ST03): primary
analysis results of a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2–3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(3):357–70.
Dutton SJ, Ferry DR, Blazeby JM et al. Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after chemotherapy (COG): a phase 3,multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 894–904.
Lockhart AC, Reed CE, Decker PA, Meyers BF, Ferguson MK, Oeltjen AR, et al. Phase II study of neoadjuvant therapy
with docetaxel, cisplatin, pani- tumumab, and radiation therapy followed by surgery in patients with locally advanced adenocarcinoma
of the distal esophagus (ACOSOG Z4051). Ann Oncol. 2014;25(5):1039–44.
Lipson EJ, Forde PM, Hammers HJ, Emens LA, Taube JM, Topalian SL. Antagonists of PD-1 and PD-L1 in cancer treatment.Semin Oncol. 2015;42(4):587–600.
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA, Pardoll DM. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade incancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(5):275–87.
Thomas Runge and Todd H. Baron. Palliative Treatment of Esophageal Cancer. Esophageal Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment.Chap 20. Pag 181-91 © Springer International Publishing AG. ISBN 978-3-319-91829-7.
Sur RK, Levin CV, Donde V, et al. Prospective randomized trial of HDR braquytherapy as a sole modality in palliation of advanced esophageal carcinoma- an international atomic agency study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;53(1):127-33.
Won JH, Lee JD, Wang HJ, et al. Self-expandable covered metallic esophageal stent impregnated with beta-emitting radionuclide:
an experimental study in canine esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;53(4):1005-13.
Lightdale CJ, Heier SK, Marcon NE, et al. Photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium versus thermal ablation therapy with Nd:YAG laser for palliation of esophageal cancer: a multicenter randomized trial. Gastroint Endoc 1995;42:507-12.
May A, Ell C. Palliative treatment of malignant esophagorespiratory fistulas with Gianturco-Z stents: a prospective clinical trial and review of the literature on covered metal stents. Am J Gastroenterol.1998;93(4):532–5.
Meredith KL, Weber JM, Turaga KK, Siegel EM, McLoughlin J, Hoffe S, et al. Pathologic response after neoadjuvant therapy is the major determinant of survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(4):1159–67.
Braghetto M, Csendes Attila, Cornejo O. Sobrevida de pacientes con cáncer de esófago sometidos a esofagectomía total torácica. Rev. méd. Chile v.128 n.1 Santiago ene. 2000.